Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are omega fatty acids?
Q2. Why omega fatty acids are called essential fatty acids?
Q3. What is so special about omega-3 then?
Q4. What is the remedy to correct this imbalance?
Q5. How can this imbalance be corrected?
Q6. Why our present edible oils are so rich in omega-6 fatty acids.
Q7. Then what is the problem with omega-6 now?
Q8. What is the remedy?
Q9. Why has omega-3 fatty acids become an endangered nutrient?
Q10. What is the role of omega 3 fatty acids in human body?
Q11. What are the good dietary sources of omega-3 fatty acids?
Q12. Are ALA, EPA and DHA equal in their action?
Q13. What about the vegetarians who are getting only ALA?
Q14. How does EPA help to maintain good health?
Q15. What is the role of Flaxseed (linseed) oil -ALA Omega-3’s in our body?
Q16. What are the limitations of Fish oil?
Q1. What are omega fatty acids?
Ans. There are two essential fatty acids namely Alpha linolenic acid (ALA;Omega-3) and Linoleic acid (LA; Omega-6). They have 18 carbons in the long fatty acid chain. They have more than one double bond (unsaturation) and hence called polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA). At their so called alpha end have carboxylic group and methyl group at their omega end. ALA has three double bonds, counted from their omega end, at 3, 6 and 9 positions. LA has two double bonds at omega minus 6 and 9 positions. Go to top
Q2. Why omega fatty acids are called essential fatty acids?
Ans. Omega -3 and omega-6 are called essential fatty acids as they cannot be synthesized in the human body. Human body has no capacity to insert double bonds at omega 3 and 6 positions. Human body cannot function normally, and cannot remain healthy, without the adequate supply of omega fatty acids in the form of food or supplement. Go to top
Q3. What is so special about omega-3 then?
Ans. Although both omega-3 and omega-6 are essential fatty acids, actually the modern man gets enough in fact too much of omega-6 and very little omega-3 fatty acids in his diet today. This imbalance is actually one of the main reasons of our ill health today. Go to top
Q4. What is the remedy to correct this imbalance?
Ans. Obviously we need to cut down omega-6 intake and increase omega-3 intake. Omega-3 fatty acids have assumed extraordinary importance for human health today and it is not surprising that omega-3 fatty acids are most sought after nutrients today. Go to top
Q5. How can this imbalance be corrected?
Ans. High omega-6 intake is usually from the edible oils used in cooking. Most of our edible oils are rich in LA. We need to choose oils, low in omega-6, preferably rich in mono-unsaturated, omega-9 (oleic acid) fatty acid. Both saturated and omega-3 fatty acids are not desirable in cooking oil as the former is cholesterogenic and the latter is very unstable to heat and gets converted to toxic peroxides. Go to top
Q6. Why our present edible oils are so rich in omega-6 fatty acids.
Ans. This is precisely because saturated and hydrogenated fat are cholesterogenic and omega-6 lowers cholesterol. Promotion of omega-6 in edible oil was to deal with cholesterol problem. Go to top
Q7. Then what is the problem with omega-6 now?
Ans. Promotion of omega-6 in last century has been a biggest blunder of twentieth century.Omega-6 and omega-3 are oppositely acting fatty acids in human body.Omega-6 is generally pro-inflammatory and omega-3 is generally anti-inflammatory. Because of excess of omega-6 and very little of omega-3 in human food chain today, inflammatory pathway is dominant in human body today in almost all part of the world, resulting in increase in incidences and severity of degenerative diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, arthritis, cancer, mental illness etc. Go to top
Q8. What is the remedy?
Ans. This is a serious but remediable public health problem. For this there has to be two pronged attack on the problem for correcting the imbalance of omega-3 and omega-6 and bring down avoidable excessive inflammation and at the same time increase the intake of omega-3 fatty acids. Go to top
Q9. Why has omega-3 fatty acids become an endangered nutrient?
Ans. Man as hunter-gatherer not too long ago in man’s history on this planet, was consuming less fat and almost equal amount of omega-6 and omega-3 fat. Omega-3 fatty acids are very unstable and have very low shelf life and in the modern world of the civilized society of packed food, omega-3 fatty is unwanted and avoided by food industry. Go to top
Q10. What is the role of omega 3 fatty acids in human body?
Ans. As mentioned above ALA is the primary, essential omega-3 fatty acid. From ALA, other omega-3 fatty acids, Eicosapentanoic acid (20 carbon EPA) and Decosahexanoic acid (22 carbon DHA) can be derived in human body.
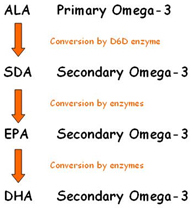
From EPA several twenty carbon anti-inflammatory fatty acids (eicosanoids) thromboxanes, leucotriens, prostagalndins and some lipid mediators are derived, and these EPA derived molecules regulate thousands of functions in human body. DHA is structural and functional constituent of membrane, brain, eye and testes. Go to top
Q11. What are the good dietary sources of omega-3 fatty acids?
Ans. Flaxseed (also called linseed) is the richest vegetarian source of ALA. Fish oil has EPA and DHA. Algae can provide DHA. Go to top
Q12. Are ALA, EPA and DHA equal in their action?
Ans. The importance of omega-3 fatty acids for human health was first established with the observation that eskimos (now called inuits) in Greenland surviving only on fatty fishes (rich in EPA and DHA) and consuming very little of carbohydrates, are protected from heart attack. As fish oil directly provided the physiologically functional fatty acid EPA and DHA, the cardio-protective nature of EPA and DHA was established in rest of the population also. Go to top
Q13. What about the vegetarians who are getting only ALA?
Ans. As mentioned above ALA is the primary essential fatty acid. It is the only form of fatty acid available to vegetarians. Obviously ALA, must meet the EPA and DHA requirements of vegetarians adequately. EPA and DHA being immediately physiologically active seems more potent. However consumption of EPA and DHA in the diet reduces the ability of conversion of ALA to EPA and DHA. Eskimos adapting to fatty fish have lost their ability to utilize ALA. ALA can further suppress the inflammatory effect of LA by inhibiting the formation of arachidonic acid (20 carbon inflammatory eicosonoids). Go to top
Q14. How does EPA help to maintain good health?
- EPA:
- Maintains normal platelet stickiness. High platelet stickiness is the first stage of clot formation which can lead to heart attacks, strokes, phlebitis and pulmonary embolism,
- Maintains arterial muscle tone, regulates blood pressure,
- Controls the inflammatory response provides relief in arthritis and psoriasis.
- Regulates sodium excretion, thereby controls water retention and provides relief in Post-Menopausal syndrome and overweight.
- Regulates immune function, provides relief in virus infections, cancer, AIDS and allergies. Go to top
Q15. What is the role of Flaxseed (linseed) oil -ALA Omega-3’s in our body?
Ans. As mentioned earlier ALA is the primary essential omega-3 fatty acid. ALA gets converted to EPA and DHA in a controlled manner wherever needed in the body and in quantities needed. Women need more EPA and DHA particularly during pregnancy and they have better ability to convert ALA to EPA and DHA. ALA further can suppress LA to AA conversion, a function, EPA and DHA in fish oil cannot perform. Go to top
Q16. What are the limitations of Fish oil?
Ans. Vegetarians cannot consume fish and fish oil. Fish oil has very high amounts of mercury contamination. Fish source is fast dwindling. From fish oil you get EPA and DHA directly and that diminishes the body’s ability to convert ALA to EPA and DHA. Go to top



